Exploring Mars distance from Earth has always fascinated scientists, researchers, and space enthusiasts alike. The Red Planet, with its mysterious terrain and potential for future human exploration, remains one of the most intriguing celestial bodies in our solar system. Understanding how far Mars is from Earth involves diving into the complexities of planetary orbits, distances, and the science behind space travel.
Our fascination with Mars dates back centuries, but modern technology has allowed us to study it in unprecedented detail. From telescopic observations to robotic missions, humanity has made significant strides in unraveling the mysteries of this distant world. The distance between Mars and Earth varies due to their elliptical orbits, making this topic even more fascinating.
In this article, we will explore everything you need to know about the distance between Mars and Earth, including how it changes over time, the methods used to calculate it, and the implications for future space exploration. Whether you're a curious beginner or an experienced astronomy enthusiast, this guide will provide valuable insights into the Red Planet's proximity to our home planet.
Read also:Roman Reigns Wife A Comprehensive Look Into Her Life And Influence
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Mars Distance from Earth
- Understanding Orbital Dynamics
- Average Distance Between Mars and Earth
- Closest Approach: Opposition and Perihelic Opposition
- Farthest Distance: Conjunction
- Methods of Measuring Mars Distance
- Historical Perspective on Mars Distance
- Implications for Future Mars Missions
- Advancements in Technology and Measurement
- Conclusion and Call to Action
Introduction to Mars Distance from Earth
Why Does Mars Distance Matter?
The distance between Mars and Earth is not just a scientific curiosity; it plays a crucial role in planning space missions, understanding planetary dynamics, and even contemplating the possibility of human colonization. Mars' varying distance from Earth is primarily due to the elliptical shape of both planets' orbits around the Sun. This means that the distance can range significantly depending on where each planet is in its orbit.
Significance in Space Exploration
For space agencies like NASA and private companies like SpaceX, knowing the precise distance between Mars and Earth is essential for planning missions. The launch windows, fuel requirements, and travel times all depend on the relative positions of the two planets. Understanding these dynamics helps optimize resources and increase mission success rates.
Understanding Orbital Dynamics
Elliptical Orbits Explained
Both Mars and Earth follow elliptical orbits around the Sun, as described by Kepler's laws of planetary motion. This means that the distance between the two planets is constantly changing. At certain points in their orbits, Mars and Earth are closer together, while at other times, they are much farther apart. This variation is due to the eccentricity of their orbits.
- Earth's orbit is nearly circular, with an eccentricity of about 0.0167.
- Mars' orbit is more elliptical, with an eccentricity of about 0.0934.
Impact on Distance
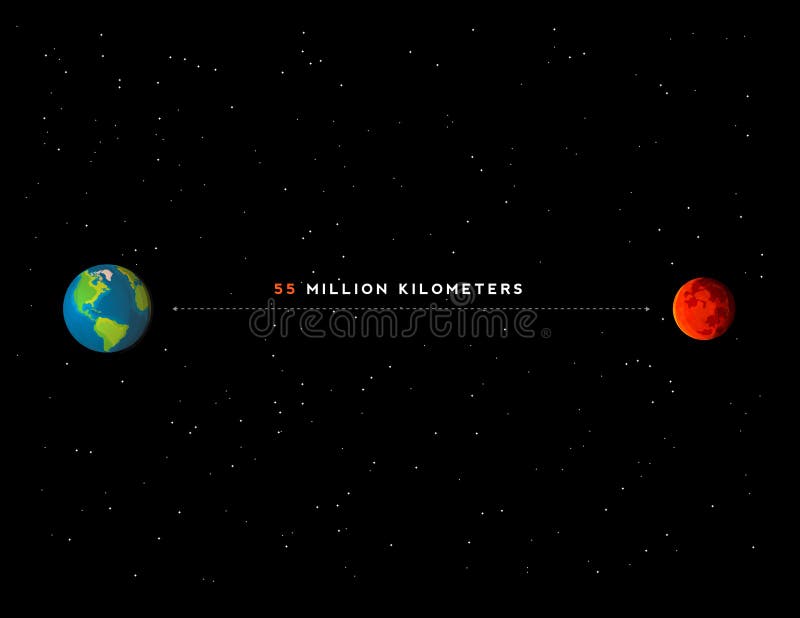
The elliptical nature of the orbits means that the distance between Mars and Earth can vary from approximately 54.6 million kilometers (33.9 million miles) at their closest approach to over 400 million kilometers (249 million miles) at their farthest separation. This significant variation has important implications for space travel and communication.
Average Distance Between Mars and Earth
Calculating the Mean Distance
The average distance between Mars and Earth is approximately 225 million kilometers (140 million miles). This figure is derived by calculating the mean of the closest and farthest distances between the two planets. While this number provides a general idea of the distance, it is important to remember that the actual distance can vary significantly depending on the planets' positions in their orbits.
Understanding Astronomical Units
Astronomers often use astronomical units (AU) to measure distances within the solar system. One AU is the average distance between Earth and the Sun, approximately 149.6 million kilometers (93 million miles). Mars is about 1.52 AU from the Sun, making its average distance from Earth roughly 1.4 AU.
Read also:Pretty Little Liars Similar Shows Dive Into The World Of Mystery And Suspense
Closest Approach: Opposition and Perihelic Opposition
Opposition Events
During opposition, Mars and the Sun are on directly opposite sides of Earth. This alignment occurs approximately every 26 months and brings Mars closer to Earth than at any other time. During a typical opposition, the distance between the two planets can be as little as 54.6 million kilometers (33.9 million miles).
Perihelic Opposition
Perihelic opposition occurs when Mars is at its closest point to the Sun (perihelion) and simultaneously aligned with Earth during opposition. This rare event brings Mars even closer to Earth, with distances as low as 54.6 million kilometers (33.9 million miles). The last perihelic opposition occurred in 2018, and the next one is expected in 2035.
Farthest Distance: Conjunction
Conjunction Defined
Conjunction occurs when Mars and the Sun are on the same side of Earth, making Mars appear directly behind the Sun from our perspective. During this time, Mars is at its farthest distance from Earth, often exceeding 400 million kilometers (249 million miles). Communication with Mars missions becomes more challenging during conjunction due to the Sun's interference.
Impact on Communication
The increased distance during conjunction not only affects travel time for spacecraft but also disrupts communication signals. Space agencies often implement communication blackouts during this period to ensure data integrity and protect spacecraft systems from potential interference.
Methods of Measuring Mars Distance
Radar Ranging
Radar ranging involves sending radio waves from Earth to Mars and measuring the time it takes for the waves to return. This method provides highly accurate distance measurements and is commonly used in modern space missions. By knowing the speed of light, scientists can calculate the distance based on the time delay.
Telescopic Observations
Historically, astronomers used telescopic observations to estimate the distance between Mars and Earth. By measuring the apparent position of Mars against background stars, they could calculate its distance using trigonometric parallax. While less accurate than modern methods, this technique laid the foundation for our understanding of planetary distances.
Historical Perspective on Mars Distance
Early Observations
Early astronomers, such as Tycho Brahe and Johannes Kepler, made significant contributions to our understanding of Mars' orbit. Their observations and calculations helped establish the laws of planetary motion, which are still used today to predict the positions of planets in the solar system.
Modern Developments
With the advent of space exploration, our knowledge of Mars' distance has become increasingly precise. Missions like NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter and the European Space Agency's Mars Express have provided valuable data on Mars' orbit and position relative to Earth. This information is crucial for planning future missions and understanding the Red Planet's dynamics.
Implications for Future Mars Missions
Challenges of Long-Distance Travel
The varying distance between Mars and Earth presents significant challenges for future missions. Travel times can range from six to nine months, depending on the launch window and mission design. This long journey requires careful planning to ensure the safety and efficiency of spacecraft and crew.
Potential for Human Exploration
As humanity looks toward the possibility of human exploration of Mars, understanding the distance and its implications becomes even more critical. Advances in propulsion technology, life support systems, and radiation protection will be essential for overcoming the challenges of long-distance space travel.
Advancements in Technology and Measurement
Role of Modern Technology
Modern technology has revolutionized our ability to measure and understand the distance between Mars and Earth. From advanced telescopes to deep-space communication networks, these tools have enabled scientists to gather precise data and make accurate predictions about planetary positions.
Looking Ahead
As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more accurate measurements and a deeper understanding of Mars' orbit and proximity to Earth. This knowledge will be vital for planning future missions and advancing our exploration of the Red Planet.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In conclusion, understanding the distance between Mars and Earth is a fascinating and complex topic with significant implications for space exploration. From the elliptical orbits of the planets to the methods used to measure their distance, every aspect contributes to our growing knowledge of the Red Planet. As we continue to explore Mars, the importance of understanding its proximity to Earth will only increase.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions in the comments below. Are you fascinated by the idea of human exploration of Mars? What do you think are the biggest challenges we face in bridging the distance between our two planets? Don't forget to explore other articles on our site for more insights into the wonders of our solar system.