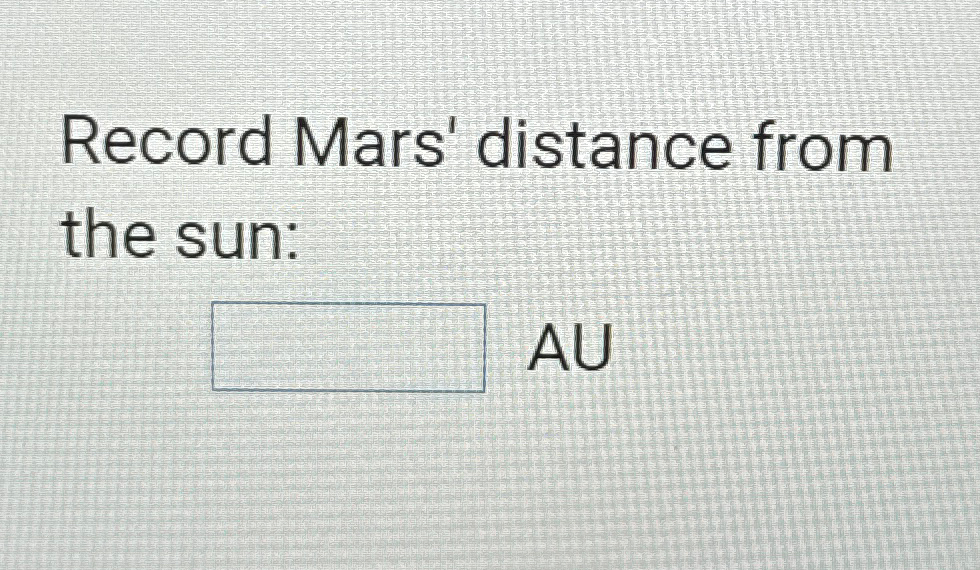
When we talk about Mars distance from Sun, we're diving into one of the most fascinating aspects of planetary science. Mars, often referred to as the Red Planet, has captivated human imagination for centuries. Understanding its orbit and distance from the Sun helps us unravel the mysteries of our solar system. In this article, we will explore this topic in-depth, providing you with valuable insights and knowledge.
Mars holds a special place in astronomy due to its proximity to Earth and its similarity to our planet in many ways. The distance between Mars and the Sun plays a crucial role in determining the planet's climate, seasons, and potential for life. As scientists continue to study Mars, they gather valuable data that enhances our understanding of the solar system's dynamics.
This article aims to provide a detailed overview of Mars' distance from the Sun, its orbital characteristics, and the implications of these factors. Whether you're a space enthusiast, a student, or simply curious about the universe, this information will deepen your appreciation for the wonders of our solar system.
Read also:Understanding The Difference Between Ipad And Tablet A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Mars: An Overview
- Mars Distance from Sun: Orbital Distance
- Aphelion and Perihelion
- Orbital Period of Mars
- Comparison with Earth's Orbit
- Impact on Mars' Climate
- Seasons on Mars
- Mars Exploration and Distance
- Future Research on Mars Distance
- Conclusion
Mars: An Overview
Mars, the fourth planet from the Sun, is a terrestrial planet with a thin atmosphere composed primarily of carbon dioxide. It is named after the Roman god of war due to its reddish appearance, which is caused by iron oxide, or rust, on its surface. Mars has fascinated astronomers since ancient times, and modern technology has allowed us to study it in unprecedented detail.
Mars' Physical Characteristics
Here are some key facts about Mars:
- Diameter: Approximately 6,779 kilometers
- Mass: About 6.42 x 10²³ kilograms
- Surface Gravity: 3.721 m/s²
- Atmospheric Composition: 95% carbon dioxide, 3% nitrogen, 1.6% argon
Mars Distance from Sun: Orbital Distance
The average distance of Mars from the Sun is approximately 227.9 million kilometers (141.6 million miles). This distance varies due to the elliptical shape of Mars' orbit, which is slightly more elongated than Earth's orbit. The distance from the Sun affects Mars' temperature, climate, and overall environment.
Elliptical Orbit and Its Implications
Mars' elliptical orbit means that its distance from the Sun changes throughout its journey. This variation influences the planet's seasons and temperature fluctuations. At its closest point to the Sun, called perihelion, Mars is about 206.6 million kilometers (128.4 million miles) away. At its farthest point, called aphelion, it is roughly 249.2 million kilometers (154.8 million miles) away.
Aphelion and Perihelion
Aphelion and perihelion are critical terms in understanding Mars' orbit. Aphelion refers to the point in Mars' orbit where it is farthest from the Sun, while perihelion is the closest point. These variations have significant implications for the planet's climate and weather patterns.
Temperature Fluctuations
During aphelion, Mars receives less solar energy, leading to colder temperatures. Conversely, during perihelion, the increased solar energy results in warmer conditions. These fluctuations contribute to the planet's seasonal changes and dust storms, which can engulf the entire planet.
Read also:The Band Cream A Timeless Legacy And Their Impact On Rock Music
Orbital Period of Mars
The orbital period of Mars, or the time it takes to complete one full orbit around the Sun, is approximately 687 Earth days. This is nearly twice as long as Earth's orbital period, which is 365.25 days. The longer orbit is due to Mars' greater distance from the Sun and the slower speed at which it travels.
Implications for Human Exploration
The orbital period of Mars affects mission planning for human exploration. Space agencies must carefully calculate launch windows to ensure that spacecraft can reach Mars efficiently. The Hohmann transfer orbit is often used to minimize fuel consumption during these missions.
Comparison with Earth's Orbit
Comparing Mars' orbit with Earth's provides valuable insights into the dynamics of the solar system. While both planets orbit the Sun in elliptical paths, Earth's orbit is nearly circular, with an average distance of about 149.6 million kilometers (93 million miles). Mars' orbit, on the other hand, is more elliptical, leading to greater variations in distance from the Sun.
Key Differences
- Average distance: Earth (149.6 million km) vs. Mars (227.9 million km)
- Orbital period: Earth (365.25 days) vs. Mars (687 days)
- Ellipticity: Earth's orbit is nearly circular, while Mars' orbit is more elongated
Impact on Mars' Climate
The distance of Mars from the Sun has a profound impact on its climate. The planet's thin atmosphere and greater distance result in much colder temperatures compared to Earth. Average surface temperatures on Mars range from -87°C to -5°C (-125°F to 23°F). The elliptical orbit also contributes to significant seasonal variations.
Seasonal Changes
Seasons on Mars last about twice as long as those on Earth due to its longer orbital period. During winter, the polar ice caps expand, while they shrink during summer. These changes are influenced by the planet's distance from the Sun and its axial tilt, which is similar to Earth's.
Seasons on Mars
Like Earth, Mars experiences four distinct seasons: spring, summer, autumn, and winter. However, the duration of each season varies due to the planet's elliptical orbit. For example, northern hemisphere summers are shorter and warmer, while southern hemisphere summers are longer and colder.
Seasonal Dust Storms
Mars is known for its massive dust storms, which can last for weeks or even months. These storms are more common during perihelion when the planet is closer to the Sun and receives more solar energy. The increased energy heats the atmosphere, creating stronger winds that lift dust particles into the air.
Mars Exploration and Distance
The distance of Mars from the Sun is a critical factor in planning missions to the planet. Space agencies such as NASA, ESA, and others must account for the planet's position in its orbit when launching spacecraft. The Hohmann transfer orbit is a common technique used to minimize fuel consumption during interplanetary travel.
Notable Mars Missions
Several missions have successfully explored Mars, providing valuable data about its surface, atmosphere, and potential for life. Some of the most notable missions include:
- Viking 1 and 2 (1976): First successful landings on Mars
- Mars Rover missions (Spirit, Opportunity, Curiosity, Perseverance): Explored the surface and searched for signs of life
- Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (2006): Provided high-resolution images and data about the planet's geology
Future Research on Mars Distance
As technology advances, scientists will continue to study Mars and its relationship with the Sun. Future missions aim to explore the planet's subsurface, search for signs of past or present life, and prepare for potential human colonization. Understanding Mars' distance from the Sun and its orbital dynamics will remain a key focus of these efforts.
Potential for Human Colonization
Colonizing Mars presents numerous challenges, including its distance from the Sun, harsh climate, and lack of resources. However, ongoing research and technological advancements are bringing this dream closer to reality. Projects such as SpaceX's Starship aim to make human missions to Mars feasible in the coming decades.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the distance of Mars from the Sun plays a crucial role in shaping the planet's climate, seasons, and overall environment. Understanding this distance and its implications is essential for scientific research and future exploration. By studying Mars, we gain valuable insights into the workings of our solar system and the potential for life beyond Earth.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and questions in the comments below. If you enjoyed this article, consider exploring other topics related to astronomy and space exploration. Together, we can continue to unravel the mysteries of the universe!